Physical Effects of Stress and Chiropractic Management
While stress is commonly perceived as primarily psychological, chronic stress produces significant physical manifestations throughout the musculoskeletal system. Understanding how prolonged stress affects the body and how chiropractic interventions may address stress-related physical symptoms can help individuals develop comprehensive approaches to managing their health.
Healthcare providers frequently observe patients whose physical discomfort correlates with chronic stress exposure, highlighting the interconnected nature of psychological and physical well-being.
How Chronic Stress Manifests Physically
Stress triggers the body's sympathetic nervous system response, commonly known as the "fight or flight" reaction. While this physiological response serves important protective functions during acute situations, chronic stress maintains this heightened state beyond normal adaptive limits, leading to various physical consequences:
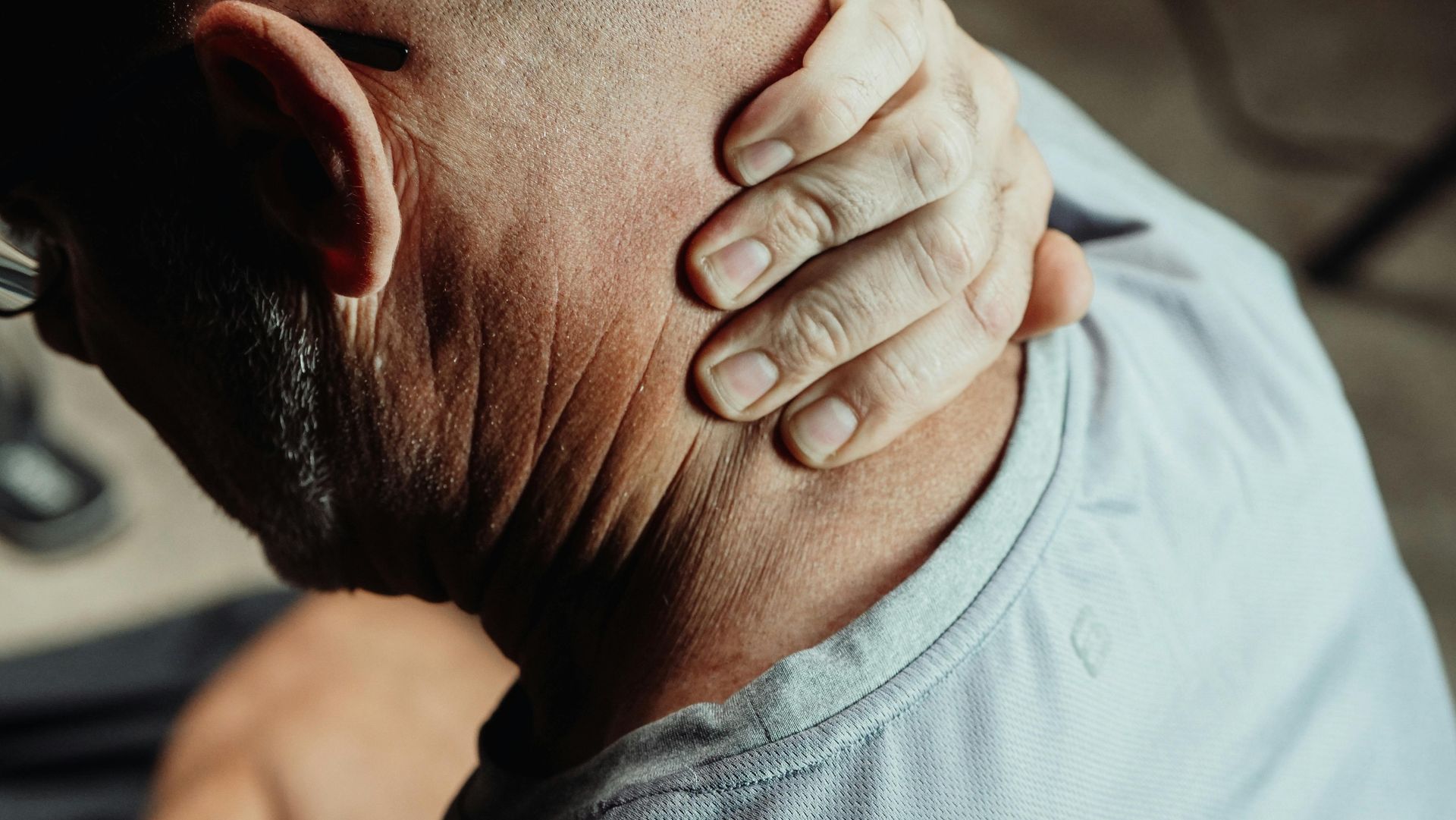
Muscular Tension: Persistent muscle contraction, particularly affecting the shoulders, neck, and lower back regions.
Tension Headaches: Recurring headache patterns often associated with cervical muscle tension and postural changes.
Bruxism and TMJ Dysfunction: Jaw clenching or teeth grinding behaviors that may contribute to temporomandibular joint discomfort and associated neck strain.
Postural Alterations: Development of forward head posture, elevated shoulders, and other compensatory postural patterns.
Sleep and Digestive Disruption: Secondary effects resulting from prolonged nervous system activation.
Reduced Range of Motion: Chronic muscular tension leading to decreased joint mobility and movement restrictions.
These physical manifestations often develop gradually and may persist even when the initial stressors are absent, indicating the need for targeted physical intervention approaches.
Chiropractic Approach to Stress-Related Physical Symptoms
Chiropractic care does not directly treat psychological stress but focuses on addressing the physical consequences of chronic stress on the musculoskeletal system. Treatment approaches aim to support the body's ability to manage stress-related physical effects through:
Joint Mobility Enhancement: Restoration of normal spinal and peripheral joint movement patterns that may be restricted due to chronic muscle tension.
Muscular Tension Relief: Addressing areas of chronic muscle tightness and associated movement restrictions.
Postural Support: Promoting more balanced spinal alignment and reducing compensatory postural patterns.
Nervous System Function: Supporting optimal nervous system communication through improved spinal alignment and reduced mechanical stress.
When spinal alignment and joint function are optimized, individuals may experience improved physical comfort and enhanced capacity for stress adaptation.
Identifying Stress-Related Physical Symptoms
Several indicators may suggest that physical symptoms have stress-related components:
Unexplained Muscle Tension: Persistent tightness in the shoulders, neck, or back without clear traumatic injury.
Pattern-Based Symptoms: Recurring stiffness or discomfort that correlates with stressful periods or high-demand situations.
Sleep-Related Issues: Difficulty achieving restful sleep or feeling physically restless despite fatigue.
Timing-Specific Headaches: Headache patterns that coincide with predictable stress periods.
Postural Awareness: Notable changes in posture during times of increased stress or emotional pressure.
Persistent Fatigue: Physical exhaustion that does not resolve with adequate rest periods.
While these symptoms may appear minor initially, chronic patterns can significantly impact functional capacity and overall quality of life.
Treatment Modalities for Stress-Related Musculoskeletal Symptoms
Chiropractic practices typically offer various interventions that may benefit individuals experiencing stress-related physical symptoms:
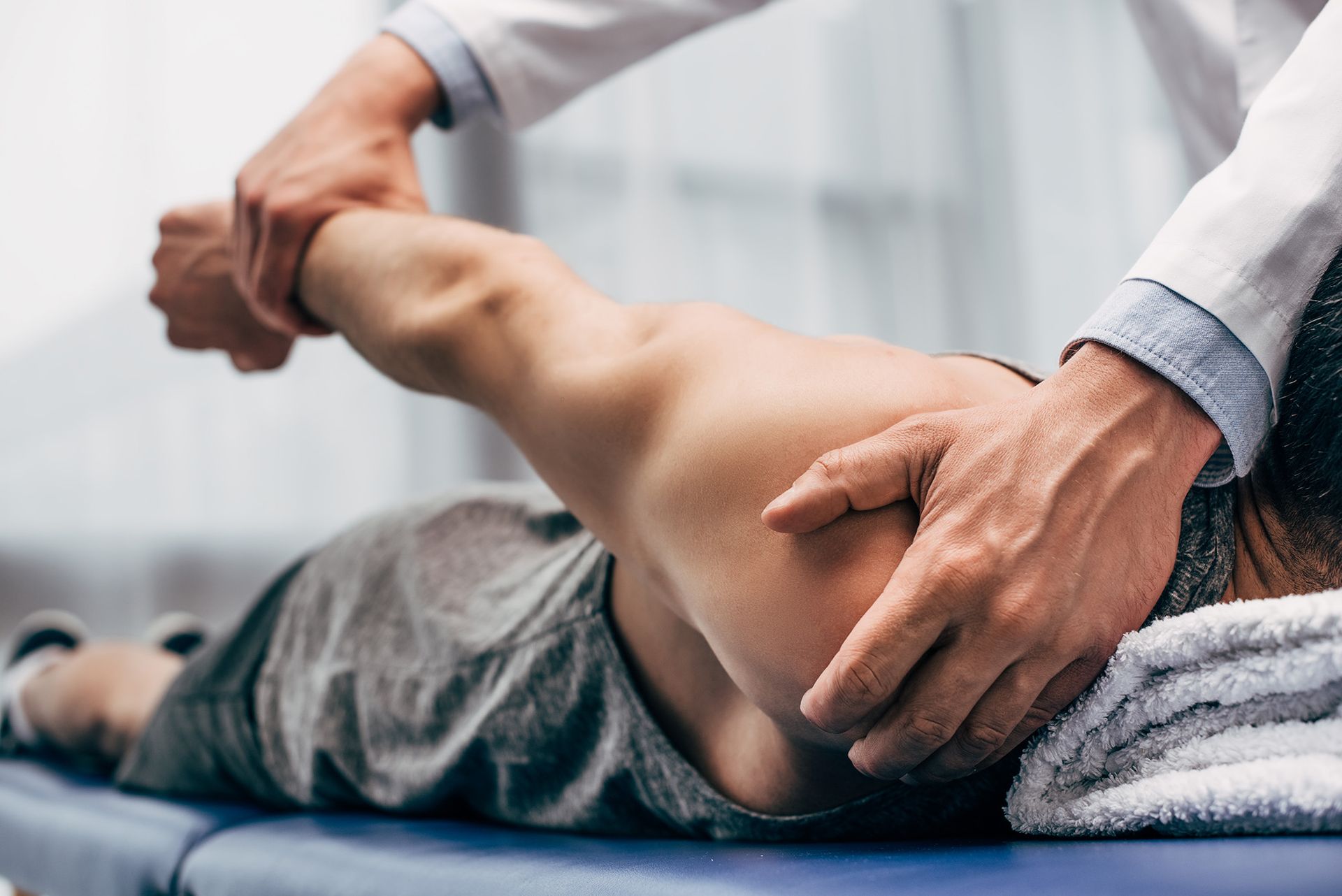
Spinal Manipulation: Manual adjustment techniques designed to restore normal spinal movement and alignment.
Electrical Muscle Stimulation: Therapeutic electrical currents applied to reduce muscle hyperactivity and promote relaxation.
Laser Therapy: Low-level laser treatments that may support tissue healing and reduce localized inflammation.
Mechanical Traction: Spinal decompression techniques that address pressure-related symptoms in the cervical and lumbar regions.
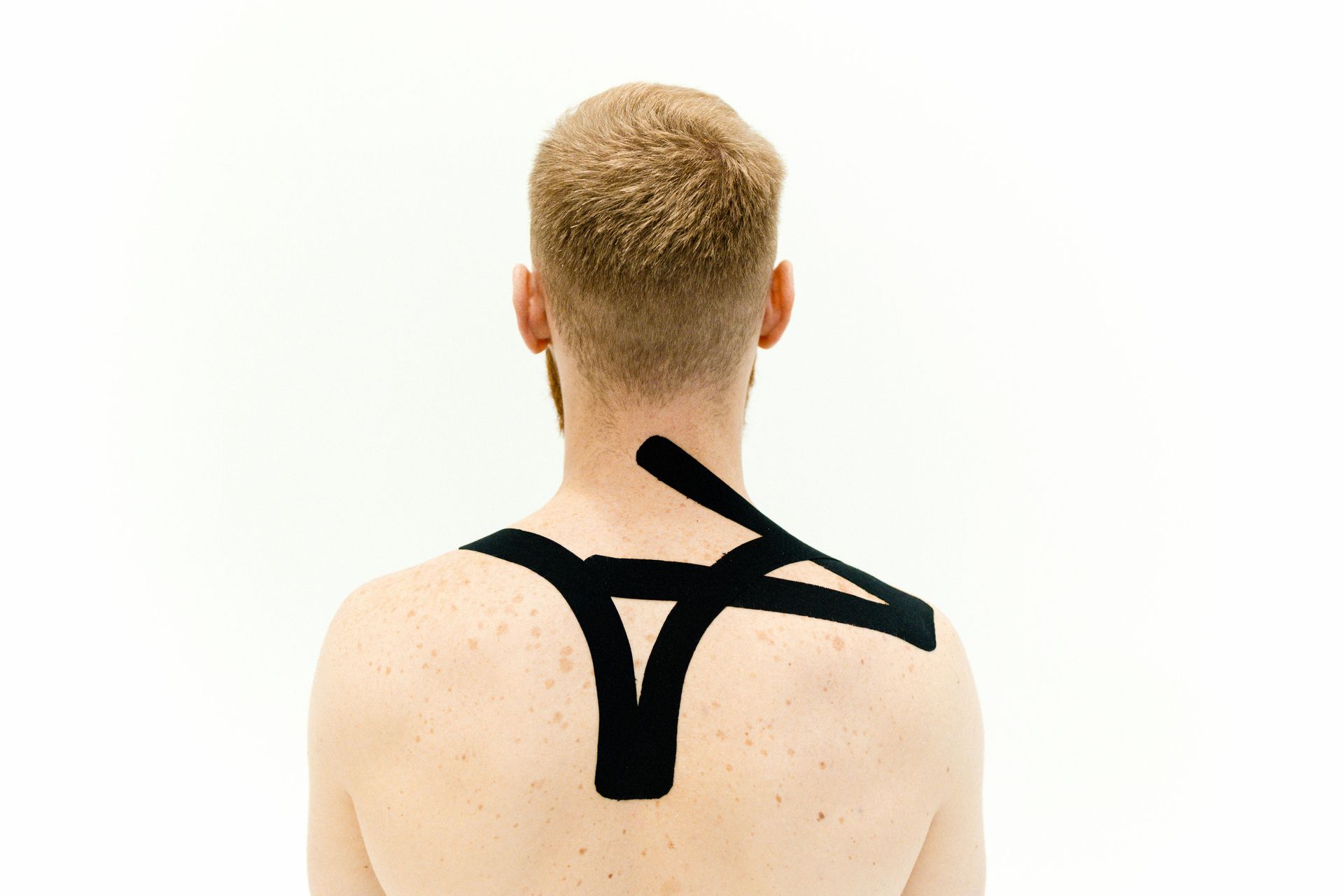
Soft Tissue Therapies: Manual techniques targeting muscle tension and fascial restrictions.
Treatment selection depends on individual presentation, symptom patterns, and patient tolerance. Professional assessment determines the most appropriate intervention strategies for each case.
Safety Considerations and Treatment Approach
Chiropractic care offers conservative, non-invasive treatment options for stress-related musculoskeletal symptoms. Treatment approaches emphasize natural movement restoration without pharmaceutical intervention, making them suitable for individuals seeking drug-free management options.
Treatment plans are individualized based on patient comfort levels, symptom severity, and functional goals. The focus remains on supporting optimal musculoskeletal function to enhance the body's capacity for stress adaptation.
Professional Evaluation Process
Initial consultations typically include comprehensive assessment of:
Symptom History: Detailed review of physical symptoms and their relationship to stress patterns.
Physical Examination: Evaluation of posture, range of motion, joint function, and areas of muscular tension.
Diagnostic Imaging: Radiographic studies when clinically indicated to assess spinal and joint structures.
Treatment Planning: Development of individualized care strategies based on examination findings and patient goals.
Professional evaluation helps determine whether chiropractic care is appropriate for addressing stress-related physical symptoms and establishes realistic treatment expectations.
Comprehensive Stress Management Perspective
While chiropractic care addresses the physical manifestations of stress, comprehensive stress management typically requires a multifaceted approach. Physical interventions may be most effective when combined with appropriate stress reduction strategies, lifestyle modifications, and other healthcare interventions as needed.
Chiropractic care serves as one component of overall health management, focusing specifically on optimizing musculoskeletal function to support the body's stress adaptation capacity.
Long-Term Considerations
Chronic stress affects individuals differently, and physical manifestations may persist even after psychological stressors are addressed. Regular musculoskeletal assessment and maintenance care may help prevent the accumulation of stress-related physical effects.
Professional guidance can help individuals understand how their bodies respond to stress and develop appropriate strategies for managing both the psychological and physical aspects of chronic stress exposure.
Understanding the connection between stress and physical symptoms empowers individuals to seek appropriate care when stress-related musculoskeletal issues develop, potentially preventing more serious complications from chronic tension patterns.